A traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when a sudden force causes damage to the brain. TBIs often arise when the head suddenly and forcefully hits an object or when an object penetrates the skull and enters the brain tissue. But acquired brain injuries (ABI) are injuries that happen to the brain where a blow or trauma was not the cause, and anoxia and hypoxia often fall under the ABI category.
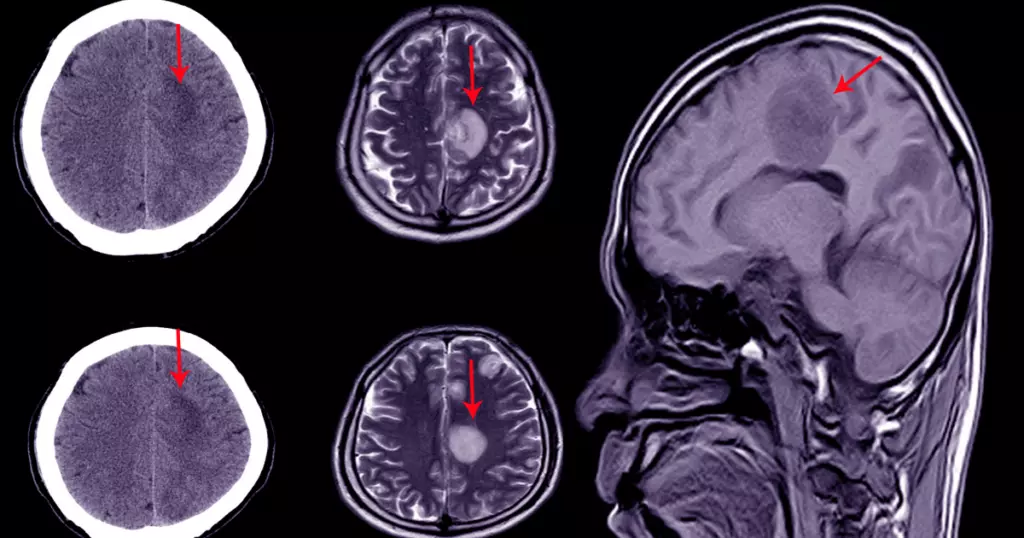
The brain requires a continuous supply of oxygen to survive because it consumes significant energy relative to its weight and size. A lack of oxygen can result in conditions such as anoxia and hypoxia. The primary difference between anoxia vs. hypoxia is the amount of oxygen deprivation a person experiences.
Brain injuries often result in life-long medical, cognitive, emotional, and psychological changes. Prompt and consistent treatment for a brain injury is crucial to mitigating the physical and financial impact of the damage on the person. Those who have suffered a TBI or ABI because of another person’s negligence should consult an experienced California personal injury attorney to determine their rights and remedies. An accident lawyer can help brain injury victims understand how the brain injury has impacted their life and secure compensation from the at-fault party.
What Is Anoxia?
Anoxia is a condition that develops when a person experiences a complete loss of oxygen to the brain. The brain needs oxygen to make glucose, the brain’s primary energy source. In most cases, oxygen deprivation will cause a victim to lose consciousness within 15 seconds, and brain cells begin to die after just four minutes.
Types of Anoxia
Anoxia is primarily the result of oxygen deprivation to the brain tissue or low oxygen content in the blood. Three psychological processes are critical to maintaining appropriate oxygen levels in the blood, which include the following:
- Perfusion: blood flow to the lungs;
- Ventilation: airflow to the lungs; and
- Diffusion: exchange of gasses between the blood and air near the lung.
Dysregulation of any of these processes can result in anoxia.
The primary types of anoxia from a brain injury include the following:
- Anemic anoxia occurs when a person’s blood cannot carry adequate oxygen around their body to keep their organs functioning;
- Anoxic anoxia happens when a person experiences a lack of oxygen in the air, such as at high altitudes;
- Stagnant anoxia occurs when a person’s blood does not reach their brain or other body parts that require oxygen; and
- Toxic anoxic happens when chemicals or poisons impact the brain’s ability to receive oxygen.
The symptoms and effects of anoxia largely depend on the area of the brain that experienced the most significant lack of oxygen.
What Is Hypoxia?
Hypoxia occurs when an organ experiences insufficient oxygen. While some tissues can adjust to temporary dips in oxygen, prolonged disruption can cause serious organ damage. Although hypoxia is less severe than anoxia, it can still result in life-threatening conditions.
Types of Hypoxia
There are four main types of hypoxia:
- Hypoxemic hypoxia occurs when a person experiences inadequate amounts of oxygen in their blood;
- Circulatory hypoxia occurs when not enough oxygen can get to a person’s tissues;
- Anemic hypoxia occurs when a person does not have sufficient red blood cells to carry oxygen; and
- Histotoxic hypoxia occurs when a person’s cells cannot use oxygen properly.
Hypoxia typically requires immediate medical treatment. Otherwise, brain tissue begins to die, which can lead to worsening brain damage or even death.
What Is the Difference Between Anoxia And Hypoxia?
Anoxia and hypoxia are often used interchangeably, as both conditions can be severe and potentially life-threatening. However, anoxia occurs when there is a complete lack of oxygen, in contrast to hypoxia, where there are inadequate oxygen levels.
Anoxia and hypoxia are both conditions related to oxygen supply to an organ’s tissues. A condition where there is an absence of oxygen supply to the tissue, even though there is adequate blood flow. A condition where there is a decrease of oxygen to the tissue, despite having adequate blood flow.
Hypoxia and Anoxia are conditions related to low oxygen levels. Hypoxia occurs when oxygen levels drop to alarmingly low levels, specifically less than 2-3 milligrams of oxygen per liter of water. On the other hand, Anoxia is a condition where oxygen levels are at zero.
Common Causes of Anoxia and Hypoxia
Anoxic and hypoxic brain injury can occur whenever a person experiences a disruption to oxygen delivery to the brain. The most common causes of anoxic and hypoxic brain injury include the following:
- Cardiac arrest,
- Traumatic vascular injuries,
- Near-drowning,
- Smoke inhalation,
- Carbon monoxide poisoning,
- Septic shock, and
- Acute lung injury.
Essentially any severe or traumatic accident or injury can result in anoxia or hypoxia.
Symptoms of Anoxia and Hypoxia
Symptoms of mild anoxia and hypoxia include the following:
- Rapid breathing,
- Alteration in skin color,
- Confusion,
- Headache, and
- Sweating.
Those who experience hypoxia may also share some of the following symptoms of anoxia:
- Breathing difficulties,
- Cognitive changes,
- Difficulty with muscle movements, and
- Decreased blood flow to essential organs.
Researchers have linked many life-threatening conditions to anoxia, such as cancer, stroke, myocardial infarction, and seizures. The most significant risk that anoxia and hypoxia pose is permanent brain damage.
Recovering Compensation for Brain Injury
Brain injuries, such as anoxia and hypoxia, present in various forms and can cause everything from mild alterations in consciousness to an unrelenting comatose state. Prognosis and recovery for brain injury victims are difficult because each case is unique. However, those who experience these injuries might require months and years of extensive and costly medical treatment.
In California, those who have experienced a brain injury because of another’s negligence can seek compensation from the at-fault party. Compensation in a brain injury case may include damages for:
- Medical expenses for things such as hospital bills, surgery costs, radiology bills, and physical and occupational therapy costs;
- Lost earnings and benefits; and
- Pain and suffering.
In some rare cases, a brain injury victim may also be entitled to punitive damages from the negligent party.
Have You Experienced a Brain Injury?
If you or a loved one were recently involved in an accident and developed a brain injury, you may be entitled to compensation from those responsible for your injuries. At GJEL Accident Attorneys, our lawyers have extensive experience working with clients who’ve suffered brain injuries, helping to connect them with meaningful compensation for everything they’ve been through and will continue to endure for the rest of their lives. Our lawyers have recovered more than $950 million on behalf of our clients, and we have a 99% success rate across all the cases we’ve handled over the years.
To schedule a free consultation with a California brain injury accident attorney, give us a call at 1-866-290-1656. You can also reach one of our personal injury attorneys by filling out our secure online contact form. Calling is free, and there is no obligation to move ahead with your case. However, if you decide to bring GJEL Accident Attorneys on board your case, we won’t collect any fees for our representation unless we can connect you with the compensation you deserve.
Visit our office nearest to you.


 AI-search
AI-search  Email
Email